A Guide to Financial Statements

At its core, the accounting equation forms the foundation of all business accounting. In practice, accountants record every financial activity according to this principle and then summarize these activities in four essential financial reports: the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, and Statement of Cash Flows. Ultimately, each statement offers a unique and vital perspective on a company’s financial health, and when viewed together, they provide a complete and detailed story.
The Accounting Equation
First and foremost, the accounting equation is the fundamental principle of double-entry bookkeeping and the basis of the Balance Sheet. We formally express it as:
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity
Simply put, this equation means that what a company owns (its assets) is equal to where those assets came from (its liabilities and equity). Alternatively, we can think of the left side (assets) as representing the company’s economic resources, while the right side (liabilities and equity) explains how those resources were obtained.
- Assets are the economic resources a company owns with the expectation of a future benefit. This includes things like cash, inventory, equipment, and buildings.
- Liabilities are the company’s financial obligations, or what it owes to others. This includes loans, accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), and other debts.
- Stockholders’ Equity represents the ownership stake in the company. It’s the residual value of the assets after all liabilities have been paid.
The Four Core Financial Statements
A complete set of financial statements includes four primary documents, each offering a unique perspective on a company’s financial position and performance.
Balance Sheet
This statement, in essence, is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a single point in time. It lists what the company owns (Assets), what it owes (Liabilities), and the ownership stake in the company (Stockholders’ Equity). It is a direct representation of the accounting equation.
Income Statement
Furthermore, also known as the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, this report shows a company’s financial performance over a period of time (e.g., a quarter or a year). It details revenues, costs, and expenses to arrive at the company’s net income (profit or loss).
Statement of Equity
Next, this statement details the changes in the ownership stake of the company over a specific period. It shows how retained earnings, dividends, and other equity transactions have impacted the total equity of the company.
Statement of Cash Flows
Finally, this statement shows how a company generates and uses cash during a specific period. It breaks the cash flow into three main activities: operating, investing, and financing.
Accounting Equations and Financial Reports
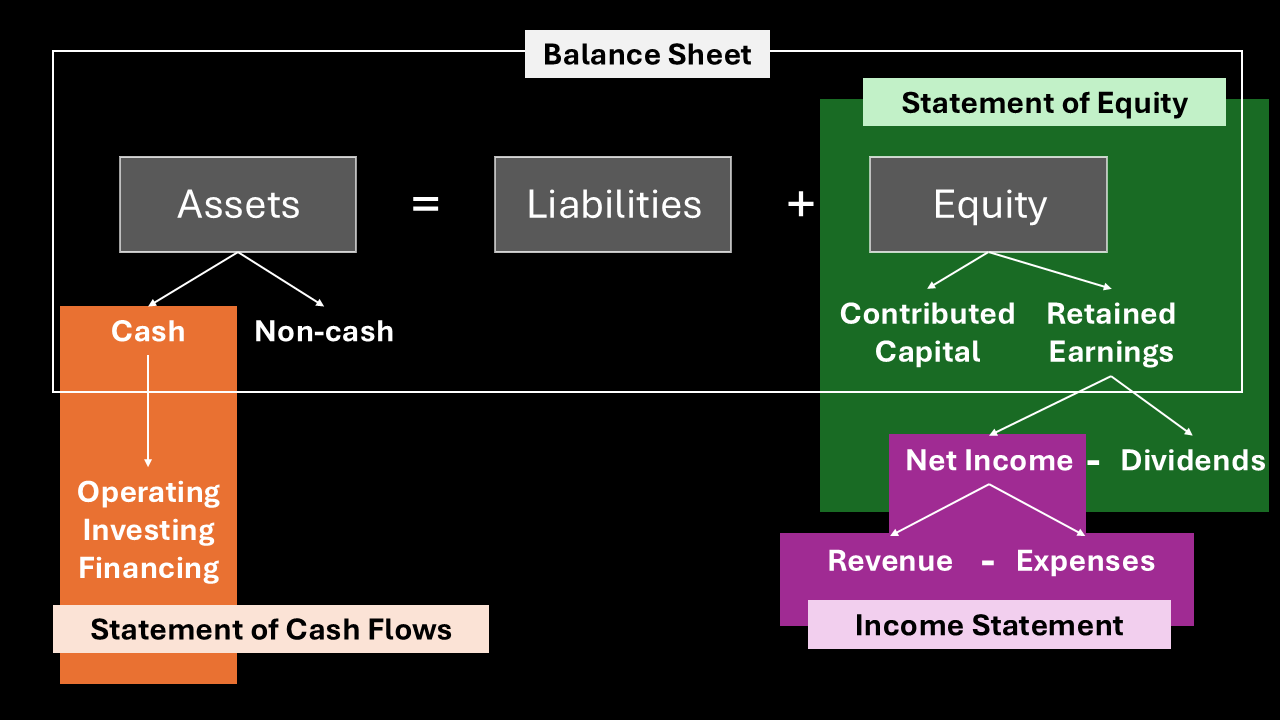
To illustrate these relationships, this diagram highlights the elements of the financial reports, their interrelationships, and the specific reports in which they appear.
- First, the accounting equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity, is the foundation of the Balance Sheet. Therefore, the Balance Sheet is a snapshot that lists a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Moreover, accountants divide assets into Cash and Non-cash categories. As a result, the Statement of Cash Flows details changes in the Cash portion, specifically classifying cash movements into operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Similarly, Equity is divided into Contributed Capital and Retained Earnings.
- While Contributed Capital represents the money that shareholders have directly invested in the company, Retained Earnings, on the other hand, is impacted by the company’s profitability. A company calculates it by taking Net Income and subtracting Dividends.
- Finally, Net Income, which is a key component of the Retained Earnings calculation, comes directly from the Income Statement. The Income Statement shows how a company’s Revenue minus its Expenses results in its Net Income.
More about Financial Statements